Model description
This is a linear regression model trained on a 2D white wine quality dataset from UCI Machine Learning Repo. The goal of this model is to predict white wine quality scores (0-10) based on 11 continuous features.
Intended uses & limitations
This model is made for assignment purposes and is not ready to be used in production.
Training Procedure
I used the scikit-learn linear regression model for this data by first splitting it into 80% training and 20% testing data, and then 75%/25% split again. The target value is quality and there are 11 numeric features. Evaluation metrics used are MSE and r2 score.
Plots
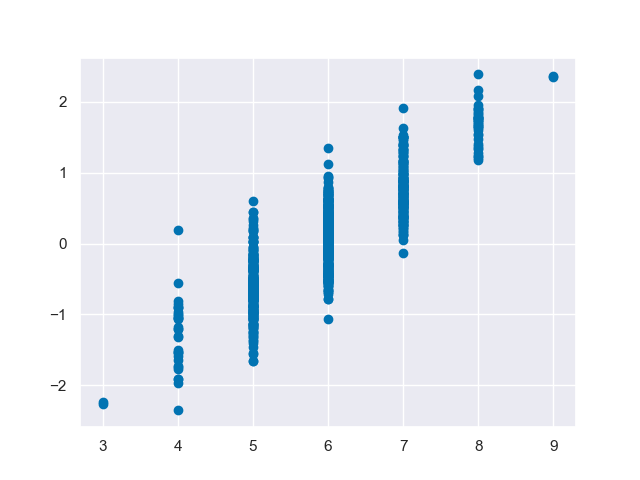 This graph above shows the residuals, here we can see a clearer pattern of an upward trend which means there might be a better model for this (as seeing no pattern is preferred in residuals). This means a linear model may not fully explain the relationship, and a nonlinear or more complex model in general would be a better model to use.
This graph above shows the residuals, here we can see a clearer pattern of an upward trend which means there might be a better model for this (as seeing no pattern is preferred in residuals). This means a linear model may not fully explain the relationship, and a nonlinear or more complex model in general would be a better model to use.
Model Plot
LinearRegression()In a Jupyter environment, please rerun this cell to show the HTML representation or trust the notebook.
On GitHub, the HTML representation is unable to render, please try loading this page with nbviewer.org.
LinearRegression()
Evaluation Results
The model used is a linear regression model designed to predict wine quality based on the continuous features, and later explroes specifically pH related to wine quality. I used MSE and r2 score as performance metrics, MSE = 0.556 and r2 = 0.313. The r2 score is pretty low meaning the model only explains about 31% of variance and shows that another model might be better to use as a linear regression model appears to be too simple. This is further backed up by the visuals. When graphing actual vs. predicted values we can see there is a slight upward trend meaning that higher actual values are corresponding to higher predicted values, whcih shows a positive correlation between the actual and predicted quality. However these points are spread far from that line which means that the model isn't that precise, but it does capture the overal direction. When graphing the residuals we can see a much more distinct linear relationship, another upward trend, indicating a more complex model would be better.
How to Get Started with the Model
Start by making a notebook for your eval, then use this starter code Dr. Brown provided:
from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download hf_hub_download(repo_id="CSC310-fall25/training_regression_wine", filename="regression.pkl",local_dir='.') dt_loaded = sio.load('regression.pkl')
from here you can use an scikit-learn estimator to do the rest of your evaluation.
Model Card Authors
Molly Croes
Model Card Contact
You can contact the model card authors through: [email protected]
Citation
This dataset is from UCI Machin Learning Repo, to learn more you can visit this link:
https://archive.ics.uci.edu/dataset/186/wine+quality
Intended uses & limitations
This model is made for assignment purposes and is not ready to be used in production.
- Downloads last month
- 22